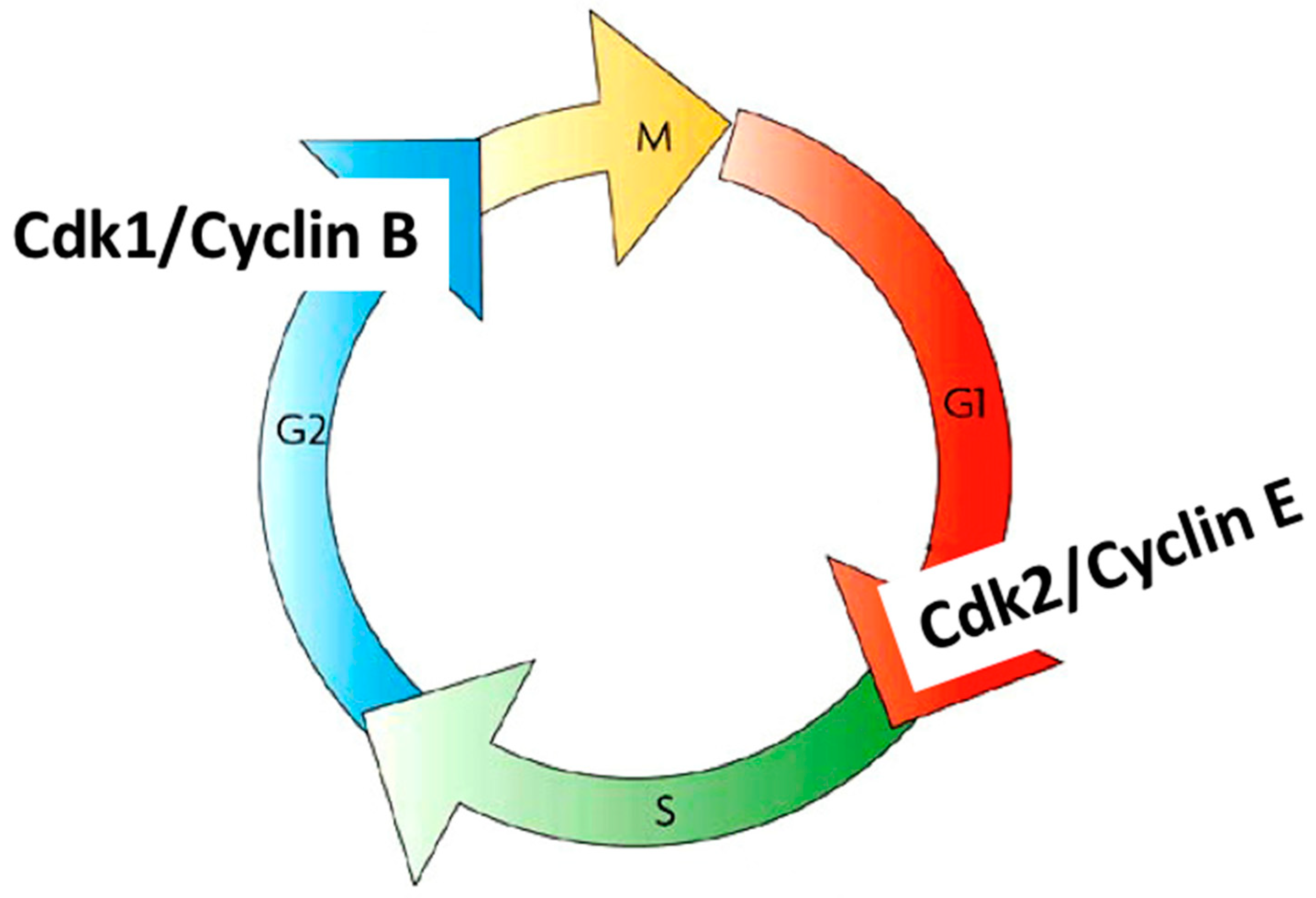
Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams Mitotic cell cycle progression is accomplished through a reproducible sequence of events, DNA replication (S phase) and mitosis (M phase) separated temporally by gaps known as G1 and G2 phases. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are key regulatory enzymes, each consisting of a catalytic CDK subunit and an activating cyclin subunit. CDKs regulate the cell's progression through the phases of the
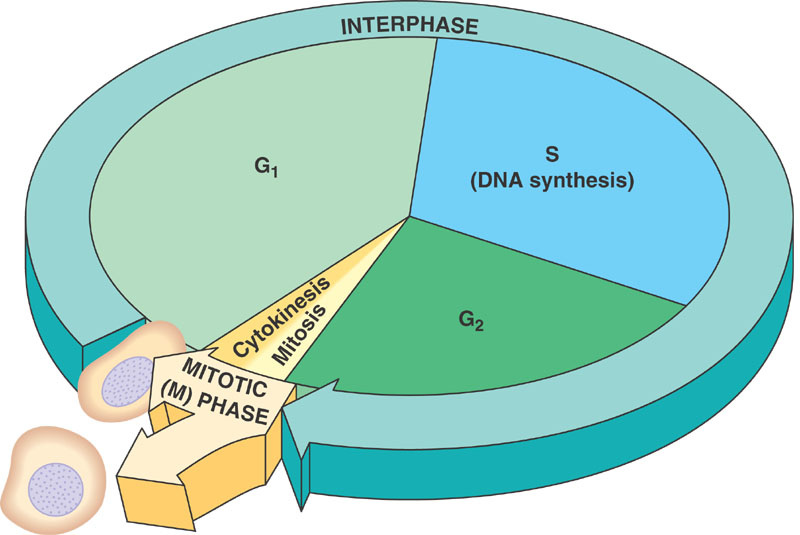
The genes affected by these mutations are known as cell-division-cycle genes, or cdc genes. Many of these mutations cause cells to arrest at a specific point in the cell cycle, suggesting that the normal gene product is required to get the cell past this point. The Gene Ontology (GO) project is a collaborative effort to address the need for consistent descriptions of gene products across databases. You can use this browser to view terms, definitions, and term relationships in a hierarchical display.

KEGG PATHWAY: Cell cycle Biology Diagrams
Cell cycle genes, and in particular S phase and checkpoint genes, are highly essential for the growth of cancer and pluripotent cells. However, checkpoint genes are also found to underlie the differences between the cell cycle features of these cell types.
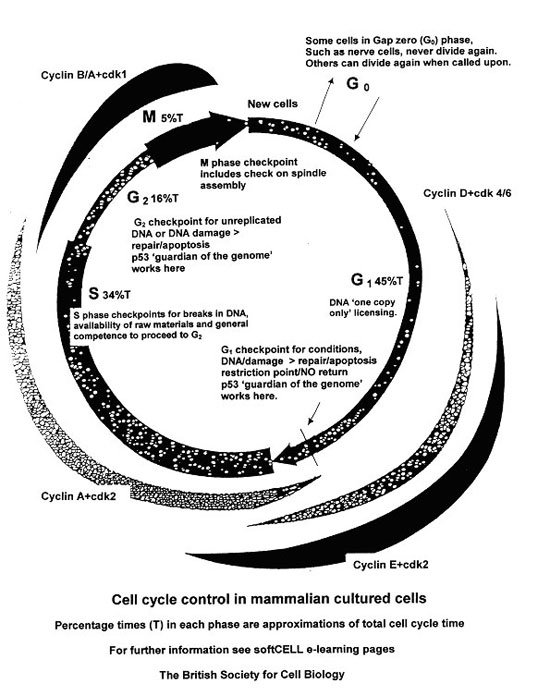
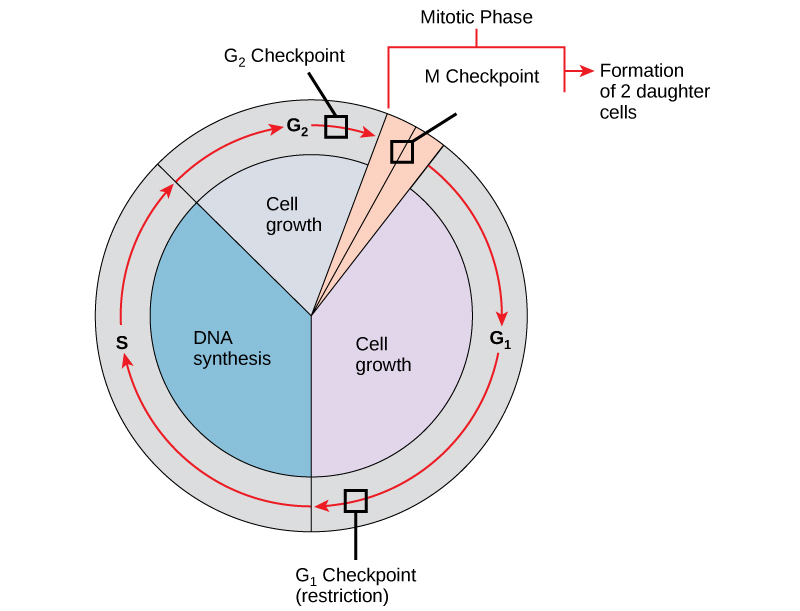
The cell cycle has checkpoints that allow genes to find problems in the cycle and prevent growth if something is wrong. Learn more about this process.
National Institutes of Health Biology Diagrams
The gene list on this page consists of all genes in the KEGG "Cell cycle - Homo sapiens (human)" pathway. Database was created by Angela Mak and Mark Knepper in the Epithelial Systems Biology Laboratory (Mark Knepper, Chief) at the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute as part of its Kidney Systems Biology Project. A list of genes used in cell-cycle regression A list of genes used in cell-cycle regression, updated with 2019 symbols
Single-cell RNA-sequencing technology gives access to cell cycle dynamics without externally perturbing the cell. Here the authors present DeepCycle,a robust deep learning method to infer the cell
